\#bond NIC이름 설정하고 네트워크 정보 설정
\#eth0과 eth1을 본딩 맴버용 NIC 추가
\#본딩 NIC 활성화
RHEL | 커널버전 |
|---|---|
| 19.5 | 4.18.0-80 |
패키지명 | 버전 |
|---|---|
| gcc | 8.2 |
| git | 2.18 |
| subversion | 1.10 |
| python | 3.6 |
| MadiaDB (XtraDB Galera Cluster 내장) | 10.3 |
| Mysql | 8.0 |
| Nginx | 1.14 |
| node.js | 10 |
| openJDK | 8, 11 |
| pacemaker | 2.0 |
| Varnish | 6.0 |
출시일자 | 커널버전 |
|---|---|
| 19.11 | 4.18.0-147 |
패키지명 | 버전정보 |
|---|---|
| php | 7.3 |
| ruby | 2.6 |
| Node.js | 12 |
| nginx | 1.16 |
| postgresql | 12 |
| .NET Core | 3.1 |
| virtio-win | |
| tpm2-tools | 2.0 |
| LLVM Toolset | 8.0.1 |
| Rust Toolset | 1.37 |
| GO Toolset | 1.12.8 |
드라이버 종류 | 모델명 |
|---|---|
| 네트워크 | Serial line internal protocol 지원 |
| 네트워크 | Baosch C\_CAN 컨트롤러 플랫폼 버스 드라이버 |
| 네트워크 | Softing DPRAM / Serial line EMS / esd 가상 CAN 인터페이스 |
| 네트워크 | SJA1000 소켓 CAN드라이버 / PLX90XX PCI 드라이버 |
| 네트워크 | Intel 2.5G 이더넷 드라이버 |
| 네트워크 | Realtek 801 무선 PCI / Core 드라이버 |
| 네트워크 | MediaTek MT76XX 장치 드라이버 |
| 그래픽+기타 | Virtual Kernel mode |
| 그래픽+기타 | Intel GTT 루틴 |
| 그래픽+기타 | Xen FrontEnd / BackEnd 페이지 디렉토리 기반 공유 버퍼 |
| 그래픽+기타 | 오디오 음소거 제어용 LED트리거 |
| 그래픽+기타 | 호스트 무선 어댑터 무선 제어 드라이버 |
| 그래픽+기타 | 네트워크 차단 장치 |
| 그래픽+기타 | Intel PCH 드라이버 |
드라이버 종류 | 업데이트 버전 |
|---|---|
| Intel Gigabit Ethernet | 5.6.0-k |
| Cisco FCoE HBA | 1.6.0.47 |
| HP Smart Array Controller | 3.4.20-170-RH3 |
| Emulex LightPulse Fibre Channel SCSI | 0.12.2.0.3 |
| LSI MPT Fusion SAS 3.0 | 28.100.00.00 |
| VMware SVGA | 2.15.0.0 |
| Broadcom MegaRAID SAS | 07.707.51.00-rc1 |
| HPE Watcgdog | 2.0.2 |
1. #### **릴리즈 정보**
2. #### **주요변경사항**
1. #### 새로운 기능
1. skopeo 명령어 기능 추가
1. sync 명령어 지원 - 컨테이너 레지스트리와 로컬레지스트리 동기화 기능 지원
2. login / logout 기능 추가
2. container.conf 지원 가능
1. 컨테이너 엔진 : /usr/shae/containers/containers.conf, /etc/containers/containers.conf 확인
2. root-less모드 엔진 : $HOME/.config/containers/containers.conf 확인
3. podman 명령어 기능 추가
1. podman system reset : podman 스토리지 초기상태로 재설정
4. rsyslog기능 추가
1. omhttp모듈을 사용해서 HTTP REST API 사용해서 메시지 전달
2. 디스크 대기열이 multi thread로 실행되어 로그처리 기능 향상
5. sudo 기능 추가
1. stdout / stderr 대신 pam 메시지를 사용자 터미널에 기록.
6. nftables 기능추가
1. python에서 api사용시 python3-nftables패키지 설치
2. ip대역 입력시 x.x.x.x/24 이외에 x.x.x.10-x.x.x.20 포맷으로도 작성 가능
7. whois 패키지를 이용해 특정 도메인 이름 혹은 ip정보 검색 가능
8. Intel OPA(Omni-Path Archituecure)호스트 소프트웨어 지원
2. #### 주요 변경사항
1. 1. tc용 eBPF 지원
2. GCroup V2 기능 지원
1. CPU 가중치및 대역폭 제한
2. 사용자 영역 메모리 및 TCP 소켓버퍼
3. I/O 리소스 분배
3. LVM 캐싱방법 지원
1. 기존 dm-cache에서 dm-writecache방식 제공
2. dm-cache : 읽기 / 쓰기 모두 캐싱해서 자주 사용하는 데이터에 대해 액세스 속도 향상
3. dm-writecache : 쓰기작업만 캐싱, SSD혹은 PMEM 디스크와 같이 빠른 볼륨에 먼저 쓰기를 저장 후 백그라운드로 디스크에 마이그레이션 수행
4. nfs 클라이언트에서 per-op오류수 확인 가능
5. pcs에서 특정 리소스만 비활성화 가능
1. pcs resource disable --simulate : 지정한 리소스 비활성화 검증
2. pcs resource disable --safe : fail-over할때 마이그레이션하는것 같이 영향받는 다른 리소스가 없을때 지정한 리소스 비활성화
3. pcs resource disable --safe --no-strict : 다른 리소스가 중지되지 않을때만 지정된 리소스 비활성화
6. pcs 기능 추가
1. pcs resource relations : 클러스터 리소스간의 관계를 트리구조로 표시
2. pcs dr : backup노드를 사용하도록 클러스터 구성된 경우 해당명령어를 통해 active와 backup모두 상태를 표시 기능 추가
3. 노드 종료시 리소스가 fail-back하지 않고 노드복구 될때까지 중지된 상태로 유지할 수 있도록 클러스터 설정값 지원
4. 단일 노드에서 클러스터 환경을 구성할 수 있도록 구성
7. samba
1. python2지원 종료
2. ctdbd서비스는 CPU thread가 90%이상 사용할때 기록
8. Wayland 기능향상 - multi GPU인식가능
9. Cockpit 기능향상
1. 15분동안 활동이 없는 경우 자동 로그아웃 기능 추가 (/etc/cockpit/cockpit.conf 파일에 timeout 설정가능)
2. SSH과 비슷하게 로그인 화면에 배더파일 내용 선택가능 (/etc/cockpit/cockpit.conf 파일에서 설정 가능)
10. 가상화 기능 향상
1. 스토리지 볼륨 생성은 모든 libvirt 유형에서 작동
2. 스토리지 풀은 LVM이나 iSCSI모두 생성 가능
3. Intel Platinum 9200시리즈 프로세스에서 KVM 사요 ㅇ가능패키지 변경사항컨테이너 기능 향상
11. 기본 레지스트리 검색 리스트 변경 (/etc/containers/registries.conf)
2. 커널 파라미터
1. NVMe장치에 대해 Hotswap 지원 가능 (커널 4.18.0-193.13.2 이상)
2. kvm.nx\_huge\_pages\_recovery\_radio= \[KVM\]
주기적으로 재핑되는 4Kib페이지수를 제거 (0은 복구 비활성화, 1이상(초단위)마다 페이지의 1/N정보 삭제
3. page\_alloc.shuffle=
페이지 할당자가 사용가능한 목록을 랜덤하게 작동하는제 제어
4. panic print =
커널패닉 발생시 시스템 정보를 출력하기 위한 비트
0 : 모든 작업정보 출력
1 : 시스템 메모리 정보
3: 타이머 정보
3: CONFIG\_LOCKDEP 기능이 켜져있는 경우 시스템 lock 정보 출력
4: ftrace 버퍼 정보 출력
5: printk 버퍼에 있는 모든 메시지 출력
5. tsx =
Intel 프로세서의 TSX기능 제어
on : TSX 기능 활성화
off : TSX기능 비활성화 (기본값)
auto : TSX가 있는 경우 비활성화하고, 그렇지 않으면 TSX활성화
6. tsx\_async\_abort =
TAA; TSX Async Abort 취약성 안화를 제어
특정 CPU모델에서 내부 버퍼 공격에 취약하기 때무넹 설정
full : TSX가 활성화된 경우 CPU에서 TAA기능을 완화
full,nosmt : 취약한 CPU에서는 TAA완화를 활성화하고, 동시 다중쓰레딩(SMT)를 비살화ㅅ화
off : 무조건 TAA완화를 비활성화 (mds=off도 활성화 필요)
7. intel\_iommu = sm\_on (기본은 off)
Intel IOMMU드라이버 DAR;Direct Memory Access Remapping 사용여부
8. mds =
full : 기본
off : TAA 영향을 받는 시스템에서 MDS를 OFF할경우 동일한 CPU취약점이 완화가능 (비활성화 할경우 tsx\_async\_abort=off로도 설정필요)
9. mem\_encrypt=
AMD 보안 메모리 암호화(SME) 제어, OFF할경우 시스템 성능이 향상될수 있지만 CPU취약점 노출가능성 존재
10. max thread
fork 항수가 생성할 수 있는 최대 스레스수 제어
3. 버그 수정
1. qdisc\_run 함수 lock시 커널 충돌 부분 해소
pfifo\_fast트래픽을 대기열에서 처리하는 과정중에 비정상적으로 종료되는 문제 해결
2. tcp\_wrappers 정보 제거
/etc/hosts.allow, /etc/hosts.deny 파일에 tcp\_wrapper패키지 정보 삭제
3. SCSI 드라이버에서 메모리 사용량 감소
일부 SCSI 드라이버가 RHEL(Cehtos)7버전보다 많은 양의 메모리를 사용했고, HBA나 vPort같은 경우에는 더 증가.
대기열 스케쥴링 개선
4. make 시 속도저하 개선
병렬 빌드시 대기하는 과정에서 응답없는 경우가 발생하는 문제 해소
5. Wayland에서 속도 저하 개선
소프퉤어 렌더러 사용할때 캐시 프레임 서버를 사용하지 않기 때문에 렌더링처리가 지연되는 문제 해결
6. Intel 10세대 CPU 지원
10세대 Intel 프로세스기반에서 VM 구동시 실패
7. RHEL7호스트에서 RHEL8 VM구성시 해당소 문제로 그래픽 출력 오류 발생 → QXL드라이버 조정을 통해 문제 해결
8. 컨테이너 레지스트리에서 quay.io 기본 경로 삭제
3. #### 주요 버전업데이트 / 추가된 패키지 리스트
출시일자 | 커널버전 |
|---|---|
| 20.4 | 4.18.0-193 |
패키지명 | 버전정보 |
|---|---|
| python | 3.8 |
| maven | 3.6 |
| HotSopt JVM용 JMC | 7.1.1 |
| rsyslog | 8.1911.0 |
| audit | 3.0-0.14 |
| sudo | 1.8.29-3.el8 |
| firewalld | 0.8 |
| nftables | 0.9.3 |
| php | 7.3 |
| GCC Toolset | 9 |
| LLVM Toolset | 9.0.1 |
| Rust Toolset | 1.41 |
| GO Toolset | 1.13 |
| grafana | 6.3 |
| samba | 4.11.2 |
드라이버 종류 | 모델명 |
|---|---|
| 네트워크 | gVNC드라이버 |
| 네트워크 | Broadcom UnuMAC MDIO버스 컨트롤러 |
| 네트워크 | iWARP드라이버 |
| 그래픽+기타 | DRM VRAM메모리 관리 모두미 |
| 그래픽+기타 | stoppoll거버너용 cpuidle드라이버 |
| 그래픽+기타 | Radeon RX5600 / RX5700 |
| 그래픽+기타 | Nvidia GTX 1650 / 1660 (TU 116 / 3D 가속지원 불가) |
| 그래픽+기타 | Matrox mgag2000 |
| 그래픽+기타 | ASPEED ast |
| 그래픽+기타 | Intel i915 |
| 그래픽+기타 | stm\_ftrace / console / core / dummy / heartbeart 드라이버 |
| 그래픽+기타 | 인텔 Tracking hub관련 드라이버 |
| 그래픽+기타 | Device DAX 드라이버 |
| 그래픽+기타 | PMEM DAX 드라이버 |
| 그래픽+기타 | Intel RAPL 코드 |
| 스토리지 | MD cluster |
드라이버 종류 | 업데이트 버전 |
|---|---|
| VMware vmxnet3 | 1.4.17.0-k |
| Intel 10G virtual | 4.1.0-k-rh8 |
| Intel 10G PC-E | 5.1.0-k-rh8 |
| Intel Ethernet E800 시리즈 | 0.8.1-k |
| NFP 드라이버 | 4.18.0-185 |
| Elastic Network Adapter | 2.1.0k |
| HPE watchdog | 2.0.3 |
| Intel I/OAT DMA | 5.0.0 |
| Emulex LightPulse Fibre Channel SCSI | 0.12.6.0.2 |
| LSI MPT Fusion SAS 3.0 | 32.100.00.00 |
| HP Smart Array Controller | 3.4.20-170-RH4 |
| QLosic Fibre HBA | 10.01.00.21.08.2-k |
| QLogic FastLinQ 4xxx FCoE | 8.42.3.0 |
| QLogic FastLinQ 4xxx ISCSI | 8.37.0.20 |
| Broadcom MegaRAID SAS | 07.710.50.00-rc1 |
출시일자 | 커널버전 |
|---|---|
| 20.11 | 4.18.0-240 |
패키지명 | 버전정보 |
|---|---|
| tuning | 2.13 |
| nginx | 1.18 |
| node.js | 14 |
| perl | 5.30 |
| php | 7.4 |
| ruby | 2.7 |
| git | 2.27 |
| Squid | 4.11 |
| GCC Toolset | 10 |
| LLVM Toolset | 10.0.1 |
| Rust Toolset | 1.45.2 |
| GO Toolset | 1.14.7 |
| OpenJDK | 11 |
| Podman | 2.1 |
| Buildah | 1.19 |
| SKopeo | 1.2.1 |
| memcached | 1.5.22 |
| libssh-lib | 0.9.4 |
| NetworkManager | 1.26.0 |
| pacemaker | 2.0.4 |
| grafana | 6.7.3 |
| samba | 4.12.3 |
| Cockpit | 4 |
| TigerVNC | 1.10.1 |
드라이버 종류 | 모델명 |
|---|---|
| 네트워크 | Mellanox ConnectX-6 |
| 네트워크 | Kvaser CAN/USB 용 CAN드라이버 |
| 네트워크 | Theobroma System UCAN 드라이버 |
| 네트워크 | Pensando NIC 드라이버 |
| 그래픽+기타 | 원격 프로세서 프레임 워크 |
| 그래픽+기타 | Intel 340x 드라이버 |
| 그래픽+기타 | Radeon RX5300 |
| 그래픽+기타 | Rizen3 4300U / 4500U / 4600U(H) / 4700U / 4800U(H) |
| 그래픽+기타 | AMD 애슬론 실버 3050U / 골드 3150U / Rizen3 3250U |
| 그래픽+기타 | Intel Tiger Lake GPU |
| 그래픽+기타 | virtio 장치용 vDPA드라이버 |
드라이버 종류 | 업데이트 버전 |
|---|---|
| megaraid\_sas | 07.713.01.00-RC1 |
| VMware vmxnet3 | 1.5.0.0-k |
| Realtek RTL8152/8153 USB드라이버 | 1.09.10 |
| Broadcom BCM573XX | 1.10.1 |
| 인텔 이더넷 스위치 호스트 | 0.27.1-ㅏ |
| 인텔 이더넷 E800 시리즈 | 0.8.2-ㅏ |
| Emulex LightPulse Fibre Channel SCSI | 0.12.8.0.1 |
| LSI MPT Fusion SAS 3.0 | 34.100.00.00 |
| HP Smart Array Controller | 3.4.20-170-RH5 |
| QLosic Fibre HBA | 10.01.00.25.08.3-k |
| Broadcom MegaRAID SAS | 07.714.04.00-rh1 |
| VMware SVGA | 2.17.0.0 |
출시일자 | 커널버전 |
|---|---|
| 21.4 | 4.18.0-305 |
패키지명 | 버전정보 |
|---|---|
| python | 3.9 |
| swig | 4.0 |
| subversion | 1.14 |
| redis | 6 |
| postgresSQL | 13 |
| Mariadb | 10.5 |
| GCC Toolset | 10 |
| LLVM Toolset | 11.0.0 |
| Rust Toolset | 1.49.0 |
| GO Toolset | 1.15.7 |
| OpenJDK | 11 |
| kabi\_whitlist | kabi\_stablelist |
드라이버 종류 | 모델명 |
|---|---|
| 네트워크 | Realtek 802.11ac (8822\*) |
| 네트워크 | Interface for UDP Encapsulated traffic |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | Regmap SoundWire |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | Intel Quick Assist / Data Accelerator |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | Oracle VM VirtualBox Graphics |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | AMD Energy repotring |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | Elastic Fabric Adapter |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | AMD PIC-E Non-Transparent Bridge |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | PCIe NTPB Performance Measurement Tool / Simple Pingpong Client / Debugging Tool) |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | Software Queue-Pair Trsnport over NTB |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | Intel Elkhart Lake PHC pinctrl/GPIO Driver |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | Dell platform setting Control interface |
드라이버 종류 | 업데이트 버전 |
|---|---|
| VMware SVGA drm | 2.18.0.0 |
| Cisco FCoE HBA | 1.6.0.53 |
| HP Smart Array Controller | 3.4.20-220-RH1 |
| Emulex LightPulse Fibre Channel SCSI | 0.12.8.0.5 |
| LSI MPT Fusion SAS 3.0 | 35.101.00.00 |
| QLosic Fibre HBA | 10.02.00.104-k |
| HPE Watcgdig | 2.0.4 |
출시일자 | 커널버전 |
|---|---|
| 21.11 | 4.18.0-348 |
패키지명 | 버전정보 |
|---|---|
| Ruby | 3.0 |
| nginx | 1.20 |
| Node.js | 16 |
| php | 7.4.19 |
| squid | 4.15 |
| rsyslog | 8.2102.0-5 |
| OpenJDK11 | 11.0.13 |
| OpenJDK8 | 8.0.312 |
| chrony | 4.1 |
| NetworkManager | 1.32.10 |
| Cmake | 3.20.2 |
| Gcc | 11.2 |
| podman | 3,3,1 |
드라이버 종류 | 모델명 |
|---|---|
| 네트워크 | SYNOPSYS DESIGNWARE Ethernet XPCS |
| 네트워크 | INTEL 10/100/1000 이더넷 PCI |
| 네트워크 | STMMAC 10/100/1000 Ethernet |
| 네트워크 | Chelsio 종료 카드의 암호화 IPSEC |
| 네트워크 | Chelsio NIC TLSD 드라이버 |
| 네트워크 | Microsoft Azure Network Adapter |
| 네트워크 | Qualcomm Atheros 802.11ax 무선 LAN 카드를 위한 코어 모듈 |
| 네트워크 | Qualcomm Technologies 802.11ax WLAN PCIe |
| 네트워크 | MAC ~ 선택 PY 연결 |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | In-Band ECC를 사용하는 Intel 클라이언트 SoC 용 MC |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | RegmapPodWire MBQ 모듈 |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | Intel 플랫폼 모니터링 기술 PMT 드라이버 |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | Intel PMT Crashlog 드라이버 |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | sysfs 시스템용 sysfs 구조 |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | Intel PMT Telemetry Driver |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | Intel PMT 클래스 Driver |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | AMD PMC Driver |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | MHI 호스트 인터페이스 |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | MHI(Modem Host Interface) PCI 컨트롤러 Driver |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | 블록 장치에 대한 vDPA 장치 시뮬레이션 |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | 네트워킹 장치에 대한 vDPA 장치 시뮬레이터 |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | Mellanox VDPA 드라이버 |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | 기본 STM framing 프로토콜 |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | MIPI SyS-T STM framing protocol driver |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | QMI 인코딩/디코더 도우미 |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | ACPI DPTF 플랫폼 전원 드라이버 |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | ACPI 플랫폼 프로파일 sysfs 인터페이스 |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | Intel Emmitsburg PCH pinctrl/GPIO 드라이버 |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | Intel Alder Lake PCH pinctrl/GPIO 드라이버 |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | MPI3 스토리지 컨트롤러 장치 드라이버 |
| 그래픽 + 기타 | 장치 매퍼 측정 서비스 |
드라이버 종류 | 업데이트 버전 |
|---|---|
| Mellanox 5세대 네트워크 어댑터 | 18.0-348 |
| Realtek RTL8152/RTL8153 기반 USB 이더넷 어댑터 | 1.11.11 |
| LSI MPT Fusion SAS 3.0 장치 드라이버 | 37.101.00.00 |
| Emulex LightPulse Fibre Channel SCSI 드라이버 | 0:12.8.0.10 |
| Qlogic 파이버 채널 HBA 드라이버 | 10.02.00.106-k |
| Microsemi Smart Family Controller | 2.1.8-045 |
| Broadcom RAID SAS Driver | 07.717.02.00-rh1 |
출시일자 | 커널버전 |
|---|---|
| 22.05 | 4.18.0-372 |
패키지명 | 버전정보 |
|---|---|
| php | 8.0 |
| perl | 5.32 |
| GCC Toolset | 11 |
| LLVM toolset | 13.0.1 |
| java | java-1.8.0 java-11 java-17 |
| bind | 9.16 |
| audit | 3.0.7 |
| pcp | 5.3.5 |
| grafana | 7.5.11 |
| grafana-pcp | 3.2.0 |
| container-tools | 4.0 |
RHEL6 (x86_64) | RHEL7 | RHEL8 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| cpu (core / Thread) | 448 | 768 | 768 |
| 최대 지원 메모리 | 12TB | 12TB (7.2이상) | 24TB |
| 최소 요구 메모리 | 1GB(cpu당 1GB필요) | 1GB(cpu당 1GB필요) | 1.5GB(cpu당 1.5GB필요) |
RHEL6 (x86_64) | RHEL7 | RHEL8 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 최소 디스크 용량 | 1GB | 10GB | 10G |
| 권장 디스크 용량 | 5GB | 20GB | 20G |
RHEL6 (x86_64) | RHEL7 | RHEL8 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 최대 파일크기 | 2TB | 2TB | 2TB |
| 최대 파일시스템 크기 | 16TB | 16TB | 16TB |
| 최대 생성 디렉토리 수 | 32000 | 32000 | 32000 |
| 최대 심볼릭링크 크기 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
RHEL6 (x86_64) | RHEL7 | RHEL8 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 최대 파일크기 | 16TB | 16TB | 16TB |
| 최대 파일시스템 크기 | 50TB | 50TB | 50TB |
| 최대 생성 디렉토리 수 | 65000 | 65000 | 65000 |
| 최대 심볼릭링크 크기 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
RHEL6 (x86_64) | RHEL7 | RHEL8 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 최대 파일크기 | 100TB | 500TB | 8EB |
| 최대 파일시스템 크기 | 300TB | 500TB | 1PB |
| 최대 생성 디렉토리 수 | 무제한 | 무제한 | 무제한 |
| 최대 심볼릭링크 크기 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
RHEL6 (x86_64) | RHEL7 | RHEL8 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BIOS | 2TB | 2TB | 2TB |
| UEFI | 16TB | 50TB | 8EB |
RHEL6 (x86_64) | RHEL7 | RHEL8 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 커널버전 | 2.6.32 ~ 2.6.34 | 3.1 | 4.18 |
| GCC | 4.4 | 4.8.2 | 8.2.1 |
| Graphic | X.org 7.4 | X.org 7.7 | Wayland 1.15 |
패스워드 입력 2회
\# selinux를 사용할 경우 레이블 변경 프로세스 설정
\#연결된 세션 중 계정명이 gogo인 계정 아숫
\# pts/10 터미널에 연결된 세션 아웃
| **모드** | **방 식** |
| 0 | - Balance-Round robin - 설정된 모든 NIC가 활성화가 되어 NIC별로 순차적으로 데이터를 전송하는 방식 - 장점 : 모든 NIC의 대역폭을 합산하기 때문에 높은 대역폭을 유지, - 단점 : NIC의 link상태를 고려하는 방식은 없기 때문에 특정 NIC의 링크가 끊어진 경우 패킷손실 가능성이 존재합니다 |
| 1 | - Active-Standby - 하나의 NIC가 활성화, 나머지는 Standby로 구성되어 데이터를 전송하는 방식 - 장점 : 높은 고가용성을 보장 - 단점 : 하나의 NIC만 활성화가 되기 때문에 네트워크 대역폭이 증가하진 않습니다. |
| 2 | - balance-xor - 기본적인 데이터 전송은 Bonding mode 0과 비슷하지만 xor연산을 이용해 특정 해시 알고리즘을 사용하여 링크에 분산시키는 방식 - bonding mode 0과 동일한 장/단점을 지니고 있습니다. |
| 3 | - broadcast - 모든 트래픽을 모든 NIC로 전송하는 방식입니다. - 장점 : 특정 NIC가 Down되어도 활성화된 NIC에서 데이터 전송을 할 수 있기 때문에 높은 고가용성 보장 - 단점 : 동일한 데이터의 중복전송이 이루어지기 때문에 높은 네트워크 비용이 발생할 수 있습니다. |
| 4 | - 802.3ad, LACP(Link Aggregation Control Protocol)를 사용하여 NIC를 묶고, 트래픽을 분산합니다. - 장점 : 높은 고가용성을 제공하여, 링크상태를 감지하여 조절합니다. - 단점 : LACP를 지원하는 Switch장비가 필요합니다. (Switch장비에서 논리적으로 Group으로 구성이 필요합니다) |
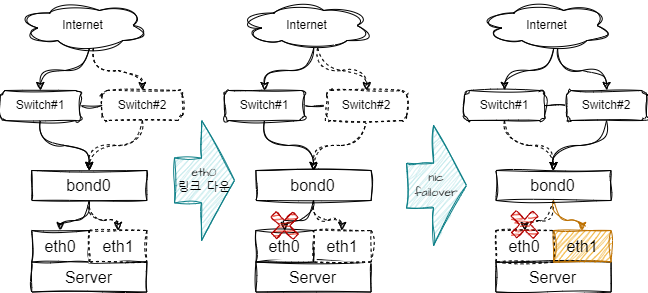 |
| - Bonding Mode 1(Active / Standby)로 구성 - Active NIC : eth0, Standby NIC : eth1, Bond NIC : bond0 |
\#eth0 브릿지 설정
\#eth1 브릿지 설정
| **스케쥴정보** | **설명** | **비고** |
|---|---|---|
| none | FIFO(선입선출) 스케쥴링 | |
| mq-deadline | 대기중인 I/O요청을 읽기 / 쓰기로 배치로 정렬 후 스케줄러에 도달하는 시점의 요청에 대해 처리 읽기 작업은 쓰기 작업보다 우선(어플리케이션에서 읽기가 지연될 경우 차단될 가능성이 높음) | 대부분 적합하나, 쓰기 작업은 비동기식으로 사용 |
| bfq | 단일 어플리케이션이 모든 대역폭을 사용하지 않도록 설정, 스토리지는 항상 유휴상태인ㄱ덧처럼 반응, 가장 낮은 대기 시간을 전달하는게 목표 | 대용량 파일을 복사하는데 적합하고, 시스템이 응답하지 않을 수 있음 |
| kyber | 모든 I/O요청 대기시간을 계산해서 각 대기시간 목표를 달성하도록 자체조정 | NVMe, SSD는 IOPS가 높은 스토리지에 적합 |
| [](http://igoni.kr/uploads/images/gallery/2023-05/rcDimage.png) |
| [](http://igoni.kr/uploads/images/gallery/2023-05/24Eimage.png) |
| [](http://igoni.kr/uploads/images/gallery/2023-05/6USimage.png) |
| [](http://igoni.kr/uploads/images/gallery/2023-05/3xdimage.png) |
| [](http://igoni.kr/uploads/images/gallery/2023-05/Zznimage.png) |
| [](http://igoni.kr/uploads/images/gallery/2023-05/2023-05-24-03-25-25.png) |
| [](http://igoni.kr/uploads/images/gallery/2023-05/6HZimage.png) |
| [](http://igoni.kr/uploads/images/gallery/2023-05/jJDimage.png) |
| [](http://igoni.kr/uploads/images/gallery/2023-05/jWVimage.png) |
| [](http://igoni.kr/uploads/images/gallery/2023-05/jbkimage.png) |
1. sysstat 패키지 설치 ```shell
$> yum install sysstat -y
```
2. sysstat정보가 수집되려면 최소 10분 이상을 기다려야 합니다.
10분주기로 말고 변경하고 싶을 경우
/etc/cron.d/sysstat 파일을 수정하면 되요. ```shell
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/cron.d/sysstat
# Run system activity accounting tool every 10 minutes
*/10 * * * * root /usr/lib64/sa/sa1 1 1
# 0 * * * * root /usr/lib64/sa/sa1 600 6 &
# Generate a daily summary of process accounting at 23:53
53 23 * * * root /usr/lib64/sa/sa2 -A
```
3. 서버 로그 export (3일에 저장된 서버 상태)
```shell
[root@localhost ~]# unset LANG
[root@localhost ~]# sar -A -f /var/log/sa/sa03 > localhost.txt
```
4. ksar내려받기 - [ksar내려받기](http://sourceforge.net/projects/ksar/)
5. ksar 실행하기 (윈도우PC에 자바가 설치되어 있어야 함)
6. 서버에 저장된 파일 불러오기 
7. 서버 정보 확인하면 끝!
$> ssh-keygen
\# qdisc 적용확인
\# Class 적용확인
\#Filter 적용 확인
\# Match (Destination 포트 정보)는 16진수로 출력
- I캐시 읽기 (Ir, 실행된 명령어 수), I1, 캐시 읽기 미스 (I1mr), LL캐시 명령어 읽기 미스 (ILmr)
- D캐시 읽기 (Dr, 메모리 읽기 수), D1 캐시 읽기 미스 (D1mr), LL 캐시 데이터 읽기 미스 (DLmr)
- D캐시 쓰기 (Dw, 메모리 쓰기 수), D1 캐시 쓰기 누락 (D1mw), LL 캐시 데이터 쓰기 누락 (Dlmw)
- 전체 프로그램에 대한 요약 통계 ```shell
——————————————————————————–
Ir I1mr ILmr Dr D1mr DLmr Dw D1mw DLmw
——————————————————————————–
6,122,264 3,538 2,481 1,725,087 79,539 16,924 655,284 10,140 8,215 PROGRAM TOTALS
```
- 기능별 통계 ```shell
——————————————————————————–
Ir I1mr ILmr Dr D1mr DLmr Dw D1mw DLmw file:function
——————————————————————————–
2,074,204 48 14 699,500 46,437 1,226 284,276 70 12 ???:do_lookup_x
```